Stakeholders
Establish responsibilities within your organisation to help improve your data maturity.
Each element of data maturity is owned by an area of the university, college or provider. Consultation, communication and support are essential to deliver effective services. Establishing responsibilities that work for your organisation is a crucial part of data management.
Some roles have overlapping areas of responsibility but with a diverging focus (for example, information management, information security and data governance). If you can agree how your university or college wants to leverage data assets, as well as how it wants to protect them, it will provide clarity for these roles and their respective responsibilities.
Key people
| Role | Essential skills | Knowledge/strengths | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy | Vice chancellor University executive board College chief executive/principal Senior leadership team College executive team Chief information officer Chief data officer Chief operating officer Director of IT Director of planning Head of ICT Head of MIS | Strategic thinking Decision making Interpretation | Institutional view Institutional memory Priorities |
| Governance | Chief information officer Registrar Head of ICT Information manager Data governance lead/officer Data analyst Data stewards Head of MIS | Conceptual clarity Attention to detail | Enterprise view Legislation Policies Processes Information assets Data assets |
| Systems and processes | Director or Head of IT Information Technology Business System Leads Business System Administrators Enterprise Architect Data Architect Business Architect | Conceptual clarity Process analysis Problem solving | Enterprise view Functional processes System tables System integrations Master data Reference data Meta data |
| Reporting | Chief data officer Director of IT/Head of IT Director of planning/BI Head of MIS/MIS Manager Business intelligence analysts Data analysts ETL developers Data warehouse developers Data warehouse architect Subject matter experts | Conceptual clarity Interpretation Business analysis Data analysis Problem solving Visual communication Reporting Software Processing software Data exploration | Enterprise view System tables Business rules Business processes Reporting definitions Datasets Statutory definitions |
| Decision making | Executive/senior leadership Team leaders All members of staff | Analysis Critical thinking Interpretation Problem solving | Functional view Functional processes Business requirements |
The roles and skills section includes information about responsibilities for reporting and data governance activities.
Responsibilities
| Executive team | Data governance lead or committee | IT | Head of MIS or head of BI | Report users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy | Responsible | Informed | Consulted | Consulted | Consulted |
| Governance | Accountable | Responsible | Support | Support | Support |
| Processes and systems | Consulted | Support | Responsible | Informed | Informed |
| Reporting | Consulted | Informed | Support | Responsible | Consulted |
| Decision making | Accountable | Informed | Informed | Support | Responsible |
Central and local ownership of activities
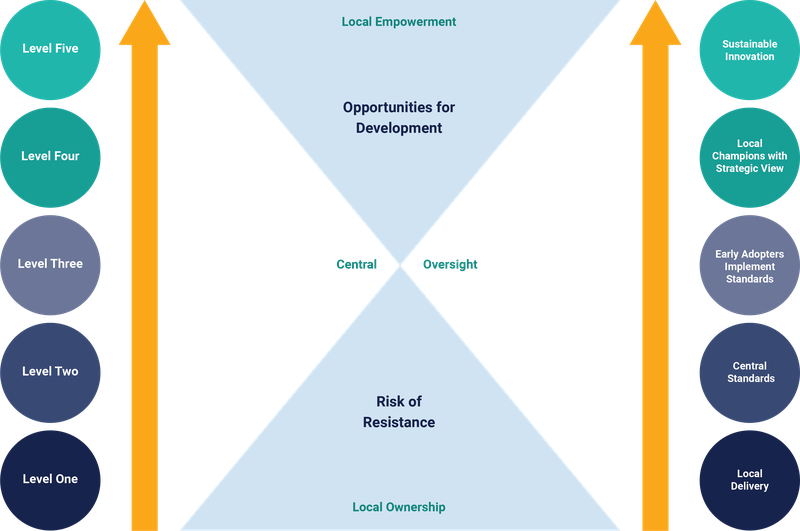
It is common that as maturity develops, the relative responsibilities of functional areas and a central service team flex. This tends to happen because at low maturity, few controls are in place and local areas can progress to their own timetable, typically leading to a combination of firefighting in some teams and innovation in others.
Finding consistency is difficult as those areas with good practice may find their independence challenged in efforts to improve and support other teams. This reality is a good example of the importance of senior vision and a strategy that has an organisational view.
Data journey
The data maturity framework incorporates five thematic elements which reflect the data journey.
The data maturity framework is copyright Jisc and made available under CC BY-NC-ND. Find out more about using content from the data maturity framework.